MARKETING NEWS
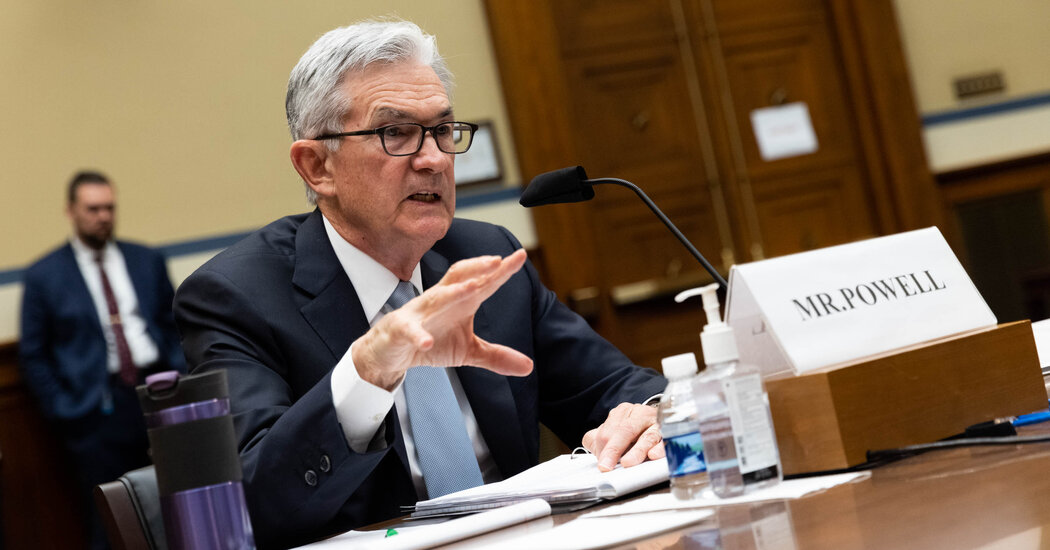
Inflation Likely to Remain High in Coming Months, Fed Chair Powell Says
Fed officials are debating when and how to slow their $120 billion of monthly government-backed bond purchases, which would be the first step in moving policy away from an emergency mode. Those discussions will continue “in coming meetings,” Mr. Powell said.Daily Business BriefingUpdated July 14, 2021, 1:29 p.m. ETThe central bank is also keeping its policy interest rate near zero, which helps borrowing remain cheap for consumers and businesses. Officials have set out a higher standard for lifting that rate from rock bottom: They want the economy to return to full employment and inflation to be on track to average 2 percent over time.The Fed’s guidance states that officials want to see inflation “moderately” above 2 percent for a time, and Mr. Powell was asked on Wednesday what that standard meant when price pressures were so strong.“Inflation is not moderately above 2 percent — it’s well above 2 percent,” Mr. Powell said of the current data. “The question will be where does this leave us in six months or so — when inflation, as we expect, does move down — how will the guidance work? And it will depend on the path of the economy.”Raising rates is not yet up for discussion, officials have said publicly and privately. The bulk of the Fed’s policy-setting committee does not expect to lift borrowing costs until 2023, based on its latest economic projections.Given Mr. Powell’s comments, that watchful stance is unlikely to shift, economists said.“We still don’t think higher inflation will result in a quicker policy tightening,” Andrew Hunter, senior U.S. economist at Capital Economics, wrote in response to Mr. Powell’s prepared testimony. “Asset purchases probably won’t start to be tapered until next year, with interest rates not raised until the first half of 2023.”The Fed is weighing the risks of higher inflation against the huge number of people who remain out of work. Congress has tasked the central bank with fostering both stable prices and maximum employment. While price pressures have picked up markedly, there are still 6.8 million fewer jobs than there were in February 2020, the month before pandemic layoffs started in earnest.
Source link